(→Main features) |
|||
| (43 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[File:Dyco96_Solvers.jpg|right|210px|Yves D'Angelo]] | |
| − | [[File:Dyco96_Solvers.jpg| | + | __TOC__ |
| − | DYCO is a suite of solvers able to compute high accuracy solutions to non-linear stock/flow potentials coupled equations | + | |
| + | |||
| + | DyCo also stands for ''Dynamiques Couplées !'' (in French). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==''The DYCO Solvers suite''== | ||
| + | DYCO is a suite of solvers able to compute high accuracy solutions to | ||
| + | non-linear stock/flow potentials coupled equations. | ||
| + | It is based on a nodal approach strategy. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | | | + | |[[File:Imuz.png|330 px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:ImuzSerie.png|110 px]] |
| − | |[[File:Sfte.png| | + | |[[File:Sfte.png|240 px]] |
|} | |} | ||
| + | Left: Elementary Cell, Coupled potentials (1 or N coupled potentials, also in series) <br/ > | ||
| + | Right: example in the thermo-electric context | ||
| − | == Main features== | + | ==''Main features''== |
* Nodal description of the considered network. | * Nodal description of the considered network. | ||
* Non linear Onsager type coupling between forces & fluxes. | * Non linear Onsager type coupling between forces & fluxes. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 26: | ||
* Handle local to global scales (i.e. from coarse-grain to fine tuning). | * Handle local to global scales (i.e. from coarse-grain to fine tuning). | ||
* Possibly complex non-homogeneous structures and topologies. | * Possibly complex non-homogeneous structures and topologies. | ||
| − | * Possibly anisotropic, discontinuous coupling coefficients; potentials | + | * Possibly anisotropic, discontinuous coupling coefficients; potentials & time dependency can also be included. |
| + | * Local flux continuity enforced | ||
* Allows for lighter/heavier computations and technological “optimization” ! | * Allows for lighter/heavier computations and technological “optimization” ! | ||
| − | == Sample Results == | + | ==''Sample Results''== |
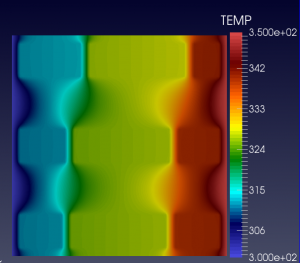
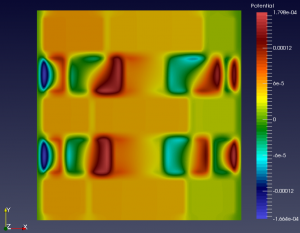
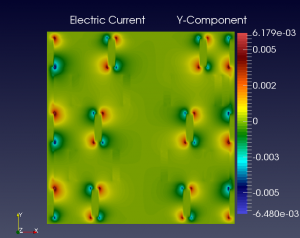
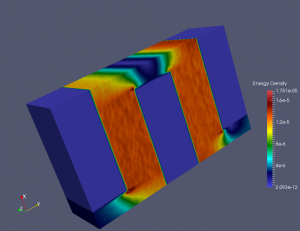
We show below a short gallery of pictures obtained using the DYCO solver, in the thermo-electric context. | We show below a short gallery of pictures obtained using the DYCO solver, in the thermo-electric context. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ Sample 3D results including a non-homogeneous thermo-electric material with non-constant TE coefficients. | |+ Sample 3D results including a non-homogeneous thermo-electric material with non-constant TE coefficients. | ||
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:OUIAlpha.png|300 px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:OUITemperature.png|300 px]] |
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ Sample 3D results including a non-homogeneous thermo-electric material with non-constant TE coefficients, continued. | ||
| + | |[[File:OUIPotential.png|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:OUIElectricCurrent.png|300 px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
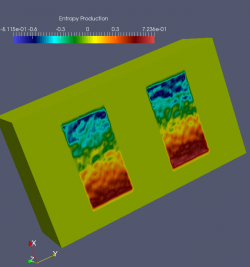
|+ Sample 3D results for N-type junction with non-constant noisy TE coefficients. | |+ Sample 3D results for N-type junction with non-constant noisy TE coefficients. | ||
| − | |[[File:OUIEnergyDensity3D.png| | + | |[[File:OUIEnergyDensity3D.png|300 px]] |
| − | |[[File:OUIEntropyProduction.png| | + | |[[File:OUIEntropyProduction.png|250 px]] |
|} | |} | ||
| − | In both cases, BC are Homogeneous Neumann and/or Non-Homogeneous Dirichlet. | + | In both cases, BC are Homogeneous Neumann and/or Non-Homogeneous Dirichlet. <br/ > |
Each elementary cell is of the non-ideal (non-linear) type. | Each elementary cell is of the non-ideal (non-linear) type. | ||
| − | ==Sub-modules == | + | ==''Sub-modules'' == |
| − | + | More specific sub-modules of DYCO shall be devoted to the numerical solution of coupled stock/flow potentials dynamics in the [http://www.dyco.fr/index.php/Ecological_Economics ecological economics] and [http://www.dyco.fr/index.php/PACS/Plant_response_to_stress_%26_Biological_Networks biological] contexts. | |
| + | |||
| − | == Participants == | + | == ''Participants'' == |
| − | Yves D'Angelo, Christophe Goupil, Eric Herbert, Xanthippi Zianni | + | [http://www.dyco.fr/index.php/User:Yd Yves D'Angelo], [http://www.dyco.fr/index.php/User:Cg Christophe Goupil], [http://www.dyco.fr/index.php/User:Eh Eric Herbert], [http://xzianni.aero.teiste.gr/ Xanthippi Zianni] |
Latest revision as of 22:10, 23 July 2023
DyCo also stands for Dynamiques Couplées ! (in French).
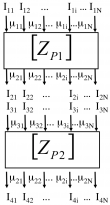
The DYCO Solvers suite
DYCO is a suite of solvers able to compute high accuracy solutions to non-linear stock/flow potentials coupled equations. It is based on a nodal approach strategy.
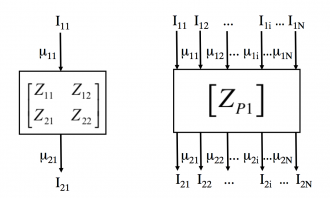
|
|
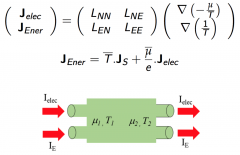
|
Left: Elementary Cell, Coupled potentials (1 or N coupled potentials, also in series)
Right: example in the thermo-electric context
Main features
- Nodal description of the considered network.
- Non linear Onsager type coupling between forces & fluxes.
- Steady, pseudo-unsteady & unsteady computations.
- Handle local to global scales (i.e. from coarse-grain to fine tuning).
- Possibly complex non-homogeneous structures and topologies.
- Possibly anisotropic, discontinuous coupling coefficients; potentials & time dependency can also be included.
- Local flux continuity enforced
- Allows for lighter/heavier computations and technological “optimization” !
Sample Results
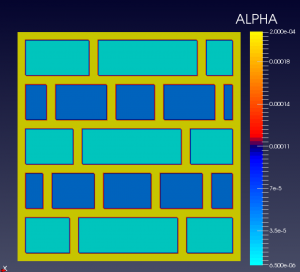
We show below a short gallery of pictures obtained using the DYCO solver, in the thermo-electric context.
|
|
|
|
|
|
In both cases, BC are Homogeneous Neumann and/or Non-Homogeneous Dirichlet.
Each elementary cell is of the non-ideal (non-linear) type.
Sub-modules
More specific sub-modules of DYCO shall be devoted to the numerical solution of coupled stock/flow potentials dynamics in the ecological economics and biological contexts.
Participants
Yves D'Angelo, Christophe Goupil, Eric Herbert, Xanthippi Zianni
